
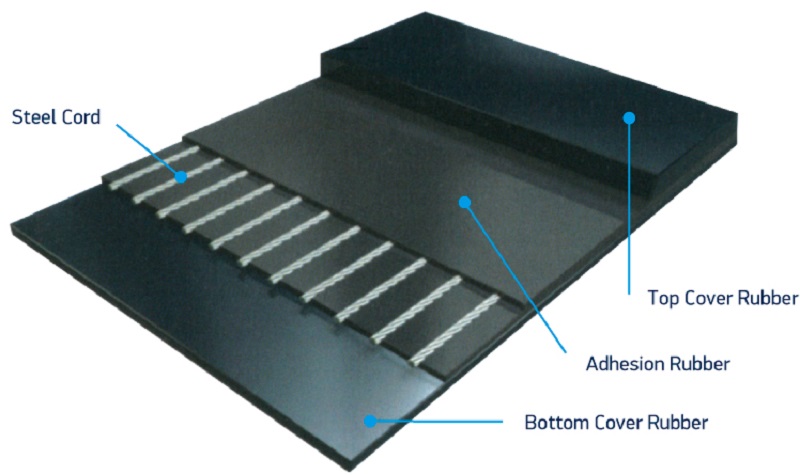
Steel cord conveyor belts are specialized conveying solutions constructed with high-strength steel cords as their reinforcing framework, encapsulated in a protective rubber coating. This unique design combines the steel cords’ exceptional tensile strength and low elongation with the rubber layer’s wear and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for heavy-load, long-distance, and harsh-environment material handling. Widely used in mining, ports, metallurgy, and other heavy industries, they efficiently meet the demands of continuous heavy-duty conveying, serving as a cornerstone of modern industrial material transport systems.
Key Features
High Tensile Strength: The embedded steel cords provide superior tensile capacity, enabling reliable use in large-span, long-distance conveying scenarios where heavy loads are standard.
Low Elongation: Minimal stretching under tension reduces the need for frequent tension adjustments, ensuring stable operation and consistent material flow.
Compact Drive Pulley Compatibility: A layer of diagonally arranged steel cords enhances bending fatigue resistance, allowing the use of smaller-diameter drive pulleys. This reduces equipment footprint and improves space efficiency.
Strong Rubber-Steel Adhesion: Steel cords undergo galvanization to strengthen bonding with the rubber layer, which tightly encapsulates them. This robust adhesion ensures stability and longevity even in harsh environments (e.g., moisture, abrasion).
Uniform Cord Tension: Special pre-treatment during manufacturing ensures steel cords are evenly arranged and have the same tension. This balance minimizes operational deviation,reducing wear and downtime.
Excellent Troughability: High transverse rigidity allows the belt to form deep, stable troughs, increasing material capacity, preventing spillage, and facilitating inspection of the underlying steel cords to avoid accidents.
Selection Guidelines
Selecting the right steel cord conveyor belt requires aligning its specifications with the unique demands of the application. Below is a step-by-step framework to guide selection:
1. Clarify Core Application Requirements
Start by defining key parameters of the operational scenario to inform specification matching:
Material Characteristics: Assess weight (heavy-load vs. light), particle size (e.g., large ore vs. fine coal), hardness (abrasive vs. soft), temperature (ambient vs. high-temperature, such as sintered ore), and chemical properties (oil, acid/alkali, or corrosive content).
Environmental Conditions: Note if the belt will operate outdoors (requiring weather resistance), underground (needing flame retardant and anti static properties), or in humid, dusty, or high-altitude settings.
Equipment Parameters: Identify conveying distance (short vs. long), drive pulley diameter, required tension, and any special structures (e.g., sidewalls, patterns) needed for the system.

2. Match Key Specifications to Needs
Based on the above requirements, target specific belt specifications to optimize performance:
Strength Grade (ST Grade)
Determined by the tensile strength of the steel cords, ST grades (e.g., ST630, ST2500, ST5400) directly correlate with load and distance:
Short-distance, light-load scenarios (e.g., in-plant conveying): Use low grades (ST630–ST1250).
Long-distance, heavy-load scenarios (e.g., mine ore transport, port bulk handling): Opt for high grades (ST1600–ST5400) to ensure tensile resistance and minimize elongation.
Cover Rubber: Thickness & Material
The rubber layer, in direct contact with materials and the environment, requires careful selection of thickness and formulation:
Thickness:
Routine use (e.g., coal, grain): 5–6mm (upper, load-bearing layer); 4–5mm (lower, non-load-bearing layer).
Heavy-wear scenarios (e.g., mine primary crushing): ≥8mm (upper); ≥6mm (lower) for enhanced impact resistance.
Special structures (e.g., sidewall belts): Increase thickness by 1–2mm to strengthen bonding with auxiliary components.
Material:
High abrasion (ore): Natural rubber and carbon black for wear resistance.
High temperature (100–200℃, e.g., sintered ore): Silicone or styrene-butadiene rubber (heat-resistant).
Oil/acid-alkali exposure: Nitrile rubber (oil-resistant) or neoprene (acid/alkali-resistant).
Underground mines: Flame-retardant rubber (compliant with standards like MT668-1997) with anti static properties.
Steel Cord Structure
Diameter & Spacing: Larger-diameter, denser-spaced cords boost load capacity but require thicker cover rubber (e.g., 17mm spacing needs ≥8.5mm cover rubber).
Differentiated Cover Rubber Design
Upper Layer (Load-Bearing): Thicker (1–2mm than the lower layer) to resist material impact and friction.
Lower Layer (Non-Load-Bearing): Thinner but engineered for anti-aging and anti static performance (e.g., ≥5mm thickness in underground mines, with conductivity testing).
3. Adhere to Standards & Customization
Compliance: Follow industry standards (e.g., China’s GB/T 9770-2001, mining’s MT668-1997) to ensure safety and performance (e.g., flame retardant, tensile strength).
Customization: For unique scenarios (e.g., ultra-high temperatures, steep inclines), collaborate with manufacturers.
Outdoor ports: 6–8mm upper EPDM rubber (weather-resistant) to withstand elements.
In summary , the industrial value of steel cord conveyor belts lies in their ability to align inherent strengths—high tensile strength, low elongation, and robust rubber-steel adhesion—with scenario-specific demands. Through precise specification matching, these belts achieve optimal durability, efficiency, and safety, making them indispensable in heavy-duty material handling.